반응형
가스 크로마토그래피(Gas Chromatography) 장치의 구조와 원리
업데이트 : 2023-05-03

개요
Sample(고체는 용매를 사용해서 녹여 쓸 수 있다. 액체, 기체도 가능하다.)
주사하는 영역(Injection port)에 넣으면 캐리어 가스(Mobile phase)가 컬럼(Column)을 지나면서 성분이 분리가 된다.
체류시간(Retention time)이 다른 것을 이용한다.
여기서 나온 Data를 Data System에 넣고 분석한다.
- Carrior Gas의 유량과 압력을 조정할 수 있다.
Moisutre trap : 가스 캐리어의 불순물(수분, 산소)을 제거하는데 쓰인다.- 산화방지를 통해 컬럼의 수명을 증가시킨다.
- Stationary phase가 컬럼 밖으로 흘러내림(bleed)을 방지한다.
- Gas Supply System
- Carrir Gas (mobile phase) : 통과하면서 분석하는 성분과 반응하면 안된다.
- 질소, 헬륨, 수소와 같이 반응하지 않는 기체를 쓴다.
- 사용하는 탐지기(Detector)에 따라 기체를 정한다.
- TCD(Thermal Conductivity Detector)에서는 수소와 헬륨을 쓴다.
- Mass Spectrometric Detector 에서는 수소를 사용해서는 안된다.
- Detector 자체에도 소량의 가스가 들어간다. (Make up gas)..table1
- A typical flow rate for a 포장 칼럼(packed column) with 3-7 mm i.d. is 25-90 mL/min and for a typical 모세관(capillary) of 0.025 mm i.d. the flow rate is around 1 mL/min.
- Makeup Gas (디텍터 안에 들어가는 기체)
- 최적조건 : Most commercially available GC detectors require 30-40 mL/ min total gas flows for best sensitivity and peak shape.
- 현재조건 : Carrier flows for capillary columns range from less than 1 mL/min to 10 mL/min
- Makeup Gas의 역할 : Carrier flows 만으로 GC 디텍터가 요구하는 가스 유량을 만들 수 없기에 보충해주는 기체이다. 민감하고 선명한 피크를 만든다.
- FID는 Maekup Gas를 태워버린다. 태우고 난 다음 남은 것을 가지고 분석한다.
- FID의 기능을 위해 수소와 공기가 필요하다. FID의 기능을 위한 Gas는 Makeup Gas와 전혀 관련이 없다. (가스 종류가 총 3개가 됐다.)
- Carrir Gas (mobile phase) : 통과하면서 분석하는 성분과 반응하면 안된다.
- Injector
- Septum :
- Septum purge line :
- Septum을 통과하는 라인.
- Septum을 청소하는 것
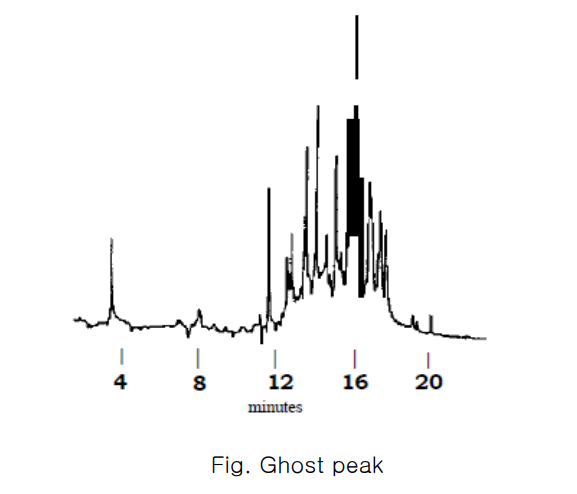
- 300℃에서 Septum을 구성하는 고무가 분해된다. (Septum bleeds)이 현상이 발생하면 baseline rise나 ghost peaks가 나타난다.
- Septum bleed is most noticeable during a temperature programmed run, because the volatiles emitted from the septum collect on the head of the column during the cool down period. These volatiles then elute during subsequent runs (under isothermal conditions, septum bleed is a continuous, steady state that appears as part of the normal background).
- Septum bleeds를 없애기 위한 것이 Septum purge line 이다.
- 샘플의 성분이나 솔벤트가 Septum에 흡수 된 것을 없애기 위한 것이 Septum purge line이다.
- 외부의 Gas가 들어오는 것을 방지하기 위해 Septum purge line이 필요하다.
- 돈이 많은 연구실은 PTFE-코딩된 Septa(Septum의 복수)를 사용한다.
- Septum purge line :
- Column을 통과하는 라인이 있고 (Capillary column)
- 빠져나가는 라인이 있다. (Split line)
- 인젝터 온도(Injector Temperature)
- 가장 휘발이 덜되어진 성분의 끓는점(B.P)보다 50 ℃ 이상 높아야 한다.
- 온도가 너무 낮았을 때의 문제
- Carry over : it occurs when the next injection backflashes and the backflashed solvent picks up some of the previously condensed compounds.
- Incomplete sample vaporization:
- 온도가 너무 높았을 때의 문제
- Sample이 부서질 수 있다. (degradation) ⇒ 분석실패
- 그래서 보통 250 ℃를 쓴다.
- Injector Discrimination : 샘플의 구성요소가 같은 속도로 기화되는게 아니기 때문에, 분석하고자 하는 샘플의 100%가 분석기에 들어가는게 아니다. 더 휘발이 잘되는 물질이 컬럼에 들어간다.
3.1. Split Injector : 샘플의 농도가 많을때 사용한다. - Split Vent : A small volume of the carrier gas flows into the column (1-4 ml/min) while a much higher volume (10-100 ml/min) flows out of the split line (split vent). - Split Ratio : column을 통과한 가스와 Split Vent로 나간 가스의 비 Typical split ratios range from 1:100 to 1:1000
3.2. Splitless Injector : 샘플의 농도가 적을때 사용한다.- 약점 : broad한 peak
- 작동 조건과 비어 있는 유리 라이너를 제외하면 분할 주입기와 동일합니다.
유리 라이너.
캐리어 가스 흐름이 낮기 때문에 피크 폭이 분할 주입기보다 더 넓어지는 경향이 있습니다(특히 더 이른 용출 피크) 분할 인젝터보다 더 넓은 경향이 있습니다.- 절차
- Purge off : peak가 broad해진다.
- Purge on : peak가 broad할때 Purge on하면 peak가 sharp해진다.
- 절차
- Sharp한 peak를 얻는 방법
- Solvent의 peak가 내 Sample의 peak와 겹치면 안된다.
- Solvent effect :
- 컬럼의 온도를 Solvent의 B.P보다 10℃ 낮게 설정한다.
- Solvent가 응축(액체화)되어진다.
- 30초 뒤에 Solvent의 B.P보다 20℃ 높게 설정한다.
- 샘플의 농도가 Solvent의 1만배여야 한다.
- Cold trapping :
- 가장 휘발성이 적은 물질의 B.P보다 150℃ 낮게 설정한다.
- 액체 질소가 주로 사용된다.
```
3.3. On-column Injector
- vaporization 없이 column에 바로 sample을 주입하는 방법
- O-가 붙은 Bio 분자들은 250℃를 잘 못견딘다.
- 정량적 분석할때 좋다.
- Column이 오염되기 쉽다. (septum이 없다.)
- !\[\[Pasted image 20230503143047.png\]\]- ![[Pasted image 20230503143326.png]]
Split vent closed가 splitless
- Columns
- Packed column
- Preparative separtation (물질분리)에 사용된다.
- Stationless stell or glass
- 흡착용으로 규조토를 많이 쓴다.
- Capillary column (모세관)
- WCOT
- Wall-coated open tubular
- SCOT
- Support-coated open tabular
- PLOT
- Porous layer open tubular
- WCOT
- Common stationary phases
- 화학적, 열적 안정하고, 샘플에 대해 좋은 용매여야 한다.
- Column bleeds, bakes되서 나오는 것을 빼야 한다.
- Nonpolar, intermediate polarity, Strongly polar
- Peak Area의 비가 sample내 성분의 비
- Packed column
- Temperature programming and Temperature&Pressure programming
- 온도, 온압력 계획
- 온도 계획
- 늦게 나오는 성분의 체류시간을 감소시킨다.
- 피크를 뾰족하게 하고, 고해상도로 한다.
- isothermal (150℃)과 Programmed temperature
![[Pasted image 20230503151840.png]]- 압력 계획 : 고압을 주면 체류시간을 감소시킬 수 있다.
- Example : 375℃에 나오는걸 325℃까지 줄일 수 있다.
- 열에 의해 잘 부서지는 물질들을 빼내기 위해서.
- 온도 계획
- 온도, 온압력 계획
- Detectors
- Response
- Signal은 component양에 따라 만들어진다.
- Sensitivitiy
- Sample이 변한만큼 Signal이 변해야 한다.
- 민감도 = Signal의 변화 / Sample의 변화
- 이 기울기가 linear해야 의미가 있다.
- FID 디텍터
- 전하량(millicoulombs) / gram of carbon
- TCD 디텍터
- mV / concentration
- S/N비 = [[S÷N Ratio]]
![[Pasted image 20230503153311.png]]
SN=2부터 Signal로 볼 수 있다.
Noise의 높이보다 signal의 높이가 2배 높아야 한다.
- Signal은 component양에 따라 만들어진다.
- Minimum Detection Limit (MDL) or Limit of Detection (LOD)
- Signal to noise를 2:1로 나오게 하는 Sample의 최소량
- Limit of quantitation (LOQ)
- Signal to noise를 10:1로 나오게 하는 Sample의 최소량
- Selectivy : 어떤 컴파운드를 디텍터가 탐지할 수 있는가
- FID : 유니버셜 디텍터
- (b) : flame phtometric dector, sulfur mode / selective detectors
- (c) : flame phtometric dector, nitrogen mode / selective detectors
- (d) : electron-caputre detector, Cl / selective detectors
- Linear and dynamic range
- analyite의 농도에 반응하는 능력
- Linearity에서 5%의 window가 있다.
- window를 벗어나는 그때의 농도 사이를 linear range라고 한다.
- dyanamic range는 더 이상 기울기가 증가하지 않는 때 까지다.
- Response
반응형
'🛒 생활정보' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 한컴 오피스 2020 체험판 다운로드 (2) | 2023.05.09 |
|---|---|
| 카카오톡 오류 발생 (0) | 2023.05.08 |
| [뱅크샐러드 유전자검사] 선착순 DNA검사 키트 배송 후기, 응모팁 (0) | 2023.05.03 |
| 책에 관한 영어권 언론사이트의 특징과 주소 모음 (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| Docker Desktop - Windows Hypervisor is not present 오류 (3) | 2023.04.30 |